Expenses are the costs of operations that a business incurs to generate revenues. When an item is ready to be sold, transfer it from Finished Goods Inventory to Cost of Goods Sold to shift it from inventory to expenses. Depending on your transactions and books, your accounts may look or be called something different. Before we dive into accounting for inventory, let’s briefly recap what inventory is and how it works. Liability accounts detail what your company owes to third parties, such as credit card companies, suppliers, or lenders. When you leave a comment on this article, please note that if approved, it will be publicly available and visible at the bottom of the article on this blog.
Double-Entry Accounting
This highlights the importance of effective procurement strategies that ensure optimal levels of inventory are maintained at all times. QuickBooks Online offers small businesses inventory tracking software to organise and keep track of inventory quantities, purchase orders, insights, valuation, and more. A key part of running a professional business is ensuring all necessary government and industry-specific laws and regulations are followed.
- Drawings represent withdrawals made by the owner from the business for personal use.
- This calls for another journal entry to officially shift the goods into the work-in-process account, which is shown below.
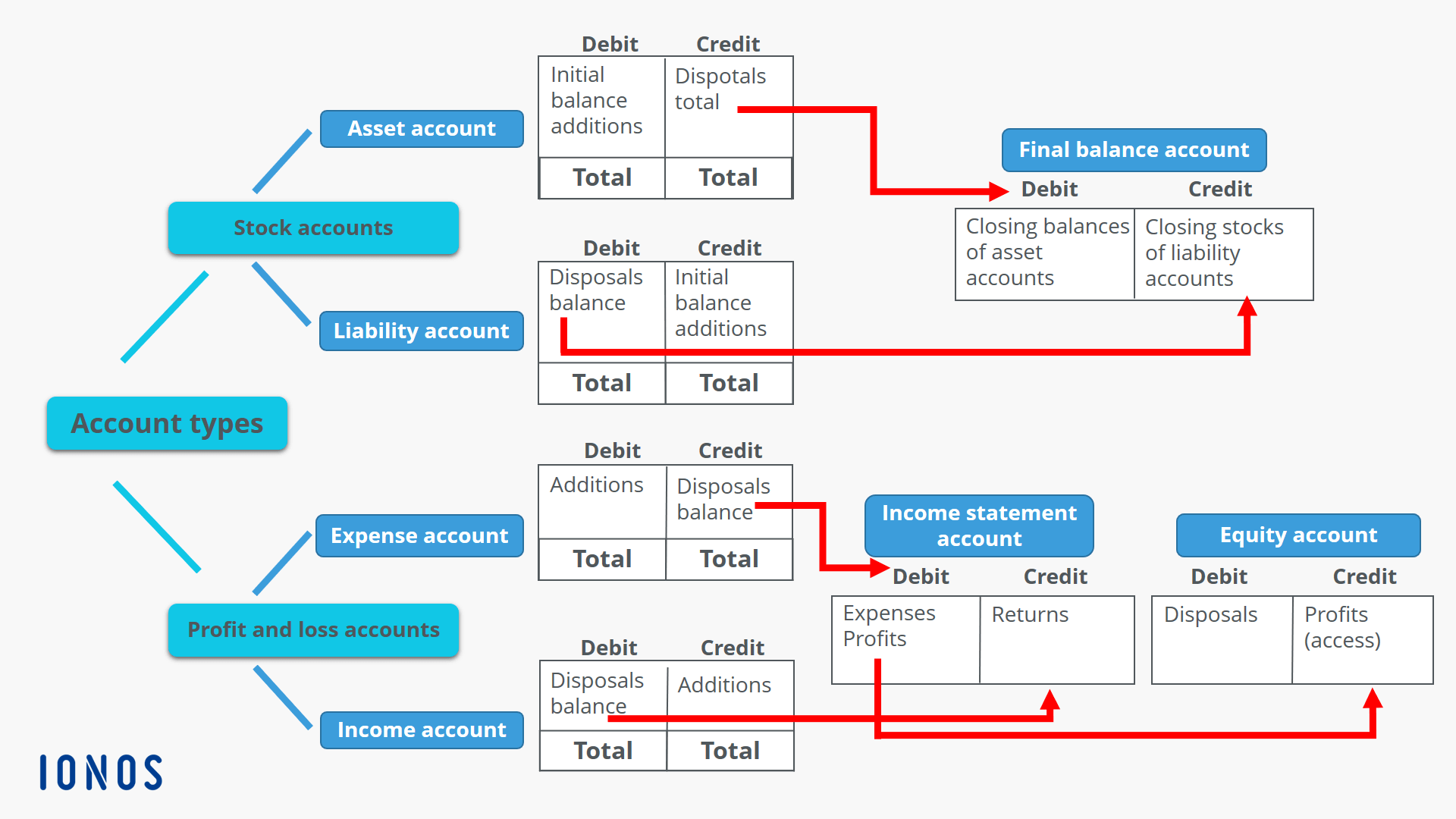
- A chart of accounts lists each account type, and the entries you need to take to either increase or decrease each account.
- This reduces the liability and increases the company’s equity through revenue earned.
- The perpetual vs periodic inventory system journal entries diagram used in this tutorial is available for download in PDF format by following the link below.
- Sal deposits the money directly into his company’s business account.
Is revenue a debit or credit?
A cost-of-goods-sold transaction is used to transfer the cost of goods sold to the operating account. Both cash and accounts receivable are asset accounts, cash is increased with a debit and the credit decreases accounts receivable. The balance sheet formula remains in balance because assets are increased and decreased by the same dollar amount.
What is a credit in accounting?
This process ensures that the financial statements show a more accurate value of assets without directly adjusting the asset’s ledger. Expenses, including rent expense, cost of goods sold (COGS), and other operational costs, increase with debits. A business posts a net profit of $20,000 at the end of the period. When a business incurs a net profit, retained earnings, an equity account, is credited (increased). As the company delivers the service monthly, it gradually recognizes $100 as revenue.
Why Is Inventory Accounting Important?
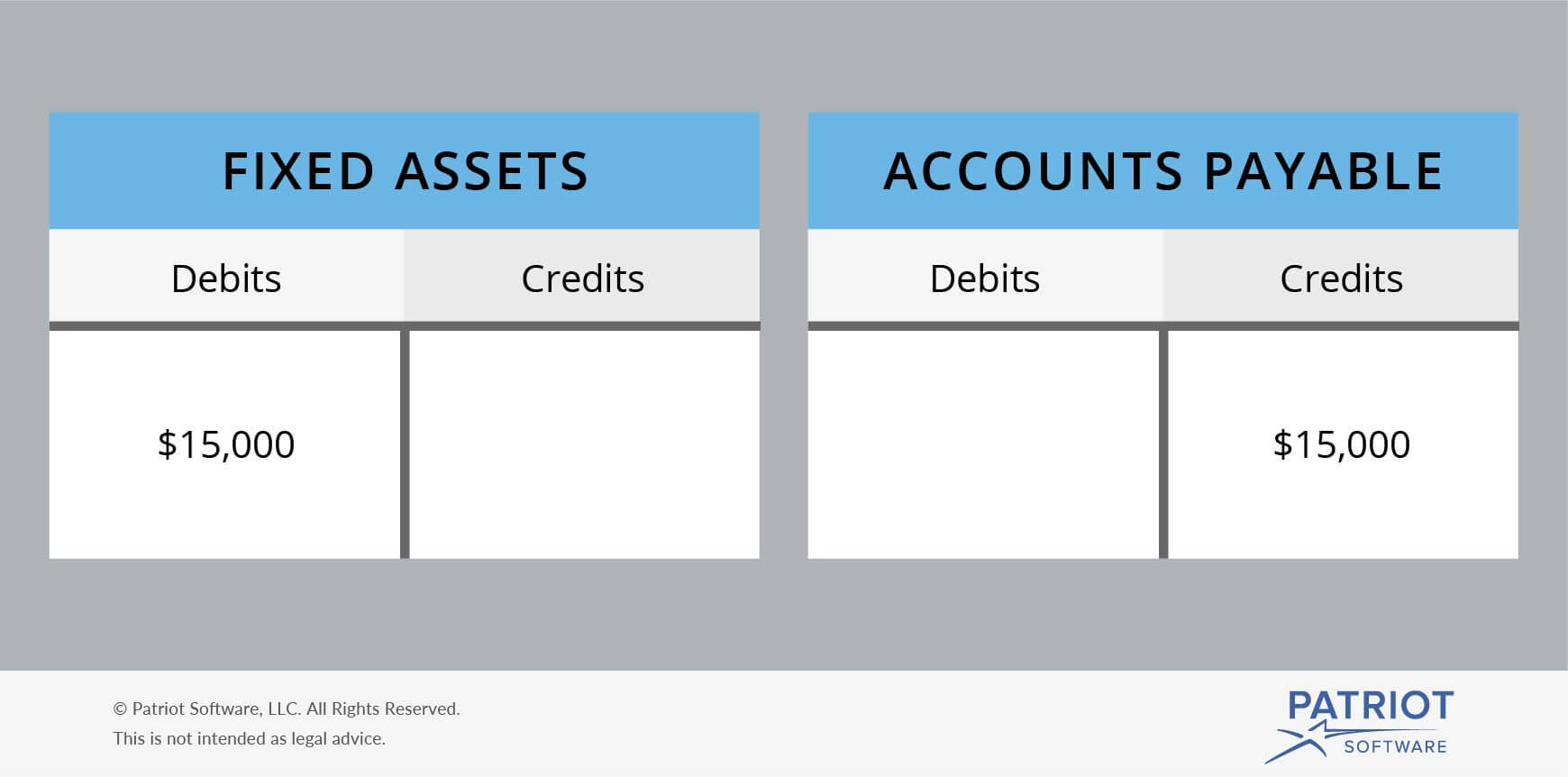
Your decision to use a debit or credit entry depends on the account you’re posting to and whether the transaction increases or decreases the account. All accounts that normally contain a credit balance will increase in amount when a credit (right column) is added to them, and reduced when a debit (left column) is added to them. The types of accounts to which this rule applies are liabilities, revenues, and equity. Technology is essential for keeping financial records accurate and current, whether managing accounts payable, generating real-time reports, or ensuring compliance. The company receives inventory (asset increases) but also incurs a liability (accounts payable).
How is Inventory Classified in Accounting?
In other words, compare your records to your bank balance to ensure everything matches. This process helps spot errors early, like missed transactions or duplicate entries and can prevent small discrepancies from turning into larger issues. The double-entry system provides a more comprehensive understanding of your business transactions.
Traditional accounting practices, like double-entry bookkeeping, still form the backbone of financial management. The money in the piggy bank decreases (cash decreases), but now they have a new asset (the toy). The double-entry bookkeeping system is built on the principle that every financial transaction affects at least 2 accounts. Debits and credits ensure that every transaction adheres to this equation, maintaining the accuracy and integrity of financial statements. You can set up a solver model in Excel to reconcile debits and credits. List your credits in a single row, with each debit getting its own column.
Keep reading through or use the jump-to links below to jump to a section of interest. The rules governing the use of debits and credits are noted below. Double-entry bookkeeping remains critical for maintaining balanced financial statements. With advanced software like Sage Intacct and AI-driven automation, businesses can better manage their accounting processes, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency.
Fortunately, accounting software requires each journal entry to post an equal dollar amount of debits and credits. If the totals don’t balance, you get an error message alerting you to correct the journal entry. Journal entry is the formal recording of financial transactions in the accounting system.
This reduces the liability and increases the company’s equity through revenue earned. This increases the child’s assets (money in the piggy bank) and creates a “liability” (an IOU to the parents). inventory debit or credit Understanding debits and credits is vital to keeping your finances in order and ensuring accurate reports. High-dollar items should be secured with locks separate from the common storage area.
Every transaction your business makes has to be recorded on your balance sheet. We’ll assume that your company issues a bond for $50,000, which leads to it receiving that amount in cash. As a result, your business posts a $50,000 debit to its cash account, which is an asset account. It also places a $50,000 credit to its bonds payable account, which is a liability account. To define debits and credits, you need to understand accounting journals.
